Scaling Docker services is actually very simple with Portainer. Jack Wallen shows you how to quickly deploy both Docker Swarm and Portainer, and then quickly scale a service to all nodes in the Swarm.

One of the many reasons why containers have taken enterprises by storm is their ability to easily scale up and down as needed. This aspect of containers is so crucial that some developers go out of their way to make it such that their deployments can auto-scale to meet demands.
But not every deployment requires that level of flexibility. For those container service deployments that could benefit from manual scaling, there’s always the command line, which isn’t at all challenging (find out how in my piece How to deploy a service to a Docker Swarm cluster).
But for those who prefer a GUI approach to all things containers, there’s my favorite management platform, Portainer. Portainer makes it even easier to scale your deployed Docker services up or down, on an as-needed basis. That’s exactly what I want to walk you through here, the scaling (up and down) of your deploy Docker services, by way of Portainer.
SEE: Hiring Kit: Cloud Engineer (TechRepublic Premium)
What you’ll need
In order to scale your services in this manner, you’ll need a running instance of Portainer deployed to a Docker Swarm. Let’s outline both the process of deploying both the Swarm and Portainer and then we’ll scale a new service.
How to deploy Docker Swarm
I’m going to distill this process down to the essentials. You’ll need at least three machines, and I’ll demonstrate on Ubuntu Server 22.04. On each machine install Docker with:
sudo apt-get docker.io -y
Make sure your user has access to the docker group (on each machine) with the command:
sudo usermod -aG docker $USER
Log out and log back in.
On the Docker controller, initialize the Swarm with:
docker swarm init --advertise-addr SERVER
Where SERVER is the IP address of the controller.
That will output the command you must run on each of the nodes to connect to the swarm. Just to make sure everything works, and we have a service to work with later, deploy a service with:
docker service create -p 8001:80 --name webservice nginx
How to deploy Portainer
We’ll now deploy Portainer. First, create a volume with:
docker volume create portainer_data
You can now deploy Portainer with the command:
docker run -d -p 8000:8000 -p 9443:9443 --name=portainer --restart=always -v /var/run/docker.sock:/var/run/docker.sock -v portainer_data:/data portainer/portainer-ce
After a minute or two, point a web browser to https://SERVER:9443, where SERVER is the IP address of the hosting server. Portainer is now ready to go.
How to scale a service with Portainer
Now that we have Docker and Portainer running, it’s time to scale that service to the Swarm. Remember, we only deployed a total of three nodes, so that’s the limit of our scaling.
Within Portainer, click Services in the left sidebar and you should see our test service we created earlier from the command line (Figure A).
Figure A
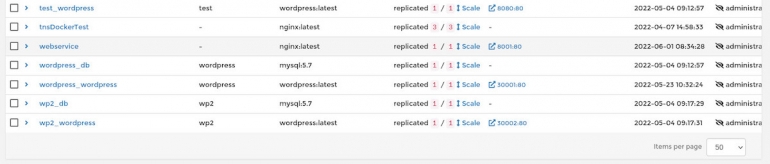
Under the Scheduling Mode column (fourth from the left), you should see a replicated 1/1 Scale. Between 1/1 and Scale there are arrows pointing up and down. To scale the service up, click the arrows and then in the resulting field either type 3 or use the up arrow to scale the service to all three nodes (Figure B).
Figure B

The service will take a moment to scale. At first it’ll read 1/3, but eventually should read 3/3, which means it has successfully scaled to all three nodes. You might have to refresh the Portainer Services page to see the service has scaled (Figure C).
Figure C

And that, my dear friends, is all it takes to scale a service with Portainer. It doesn’t get much easier than that.
Subscribe to TechRepublic’s How To Make Tech Work on YouTube for all the latest tech advice for business pros from Jack Wallen.
